Selecting the right display technology for your TV, monitor, or devices can significantly impact your viewing experience. The two primary display technologies are OLED and LCD, each with its own unique features that cater to different needs and preferences. In this article, we will explore these two types of display technology, helping you make informed decisions based on your specific application.
Key Takeaways
- OLED offers better contrast and color.
- LCDs are generally more affordable.
What Is OLED, And What Is LCD?
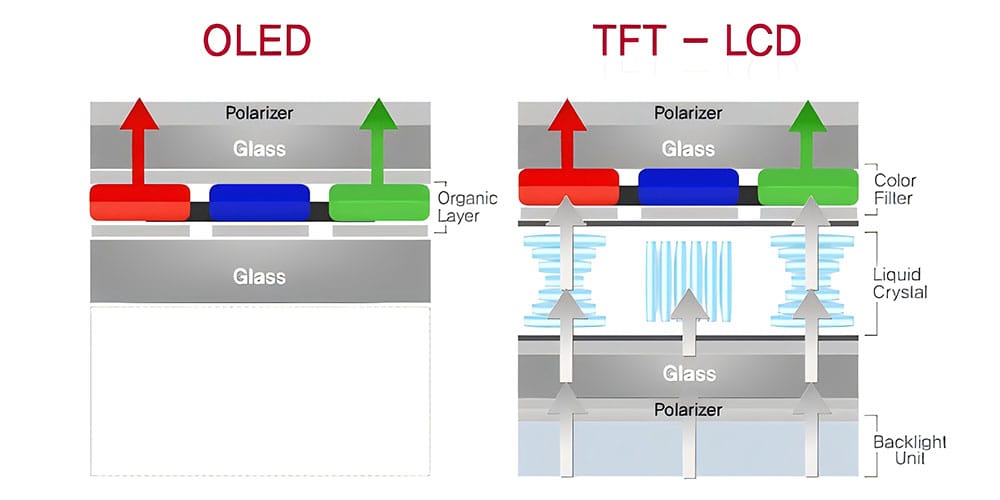
OLED, short for Organic Light Emitting Diode, utilizes organic materials that emit light when electricity is passed through them. This allows each pixel to turn on and off independently, leading to true blacks and vibrant colors. LCDs, or Liquid Crystal Displays, use a backlight to illuminate pixels, which can result in less contrast but often greater brightness in well-lit environments.
Related: Types of LCD
OLED Vs LCD Displays: What’s the Difference?
Choosing between OLED and LCD involves evaluating factors like contrast ratio, color gamut, and black levels. Additionally, consider aspects such as resolution, refresh rate, brightness, viewing angles, response time, lifespan, risk of burn-in, energy efficiency, and cost.
Contrast Ratio
The contrast ratio directly affects the depth and realism of the image. OLED displays offer an infinite contrast ratio because they can turn pixels completely off, achieving true blacks. LCDs, on the other hand, rely on a backlight, which limits their contrast ratio from 1000:1 to 5000:1. This means that blacks on an LCD are often backlit, appearing more grayish compared to OLEDs.
Color Gamut
Color gamut influences how vibrant and diverse the display colors appear. OLED screens provide a wide color gamut, delivering rich and vibrant colors perfect for colorful content like movies or games. Can reach 100% DCI-P3. LCD panels can also display good color quality, but less than OLED.
Black Levels
Black levels are crucial for viewing scenes with dark visuals. OLED technology excels in displaying true black since each pixel can emit its own light or turn off completely, ensuring no light bleed. LCDs are limited by their backlight, which can cause blacks to appear less deep and more grayish.
Resolution
Both OLED and LCD screens support high resolutions, including up to 8K. OLED displays offer sharp and detailed images, making them suitable for media that benefit from high resolution. Likewise, LCDs handle high-resolution content effectively.
Refresh Rate
Refresh rate is important for smooth video and gaming experiences. OLED screens typically feature higher refresh rates, which is advantageous for gaming and fast-paced content. LCDs can also provide good refresh rates, but performance may vary with different panel technologies, like IPS, TN, or VA.
Brightness
Brightness affects how well you can see the display in bright environments or direct sunlight. OLED displays have decent brightness levels but may not be as effective as LCDs in very bright conditions, especially outdoors. High-end OLED panels (e.g., in premium smartphones and TVs) can reach 1,200–2,000 nits.
LCDs, with their backlighting, can produce higher brightness, making them suitable for well-lit environments. Some high-end or specialized LCDs (e.g., for outdoor use) can reach 2,000–3,000 nits.
Viewing Angles
Viewing angles determine how good the image looks off-center. OLED screens offer wide viewing angles, maintaining color consistency and brightness even when viewed from the side. LCDs, particularly TN panels, tend to have limited viewing angles, where colors can shift or wash out.
Response Time
Response time affects how quickly the display can change pixels, which is crucial for fast-moving content. OLED screens often have faster response times, less than 1ms, making them ideal for gaming or watching sports. LCDs generally have good response times, but these can vary by panel type, typically 1 ms to 5 ms. If you value crisp motion and minimal blur, response time should be a consideration.
Lifespan
The expected lifespan of a display technology can affect its long-term value. OLED displays typically have a shorter lifespan due to risks like burn-in and pixel degradation. In contrast, LCD panels generally offer longer, more stable performance over time (can be over 100,000 hours).
Risk of Burn-In
Burn-in occurs when static images leave permanent marks on the screen. OLED displays have a higher risk of burn-in, especially if static content is frequently displayed. LCD panels are less susceptible to burn-in, making them a safer option for static content. If your use includes static images, burn-in risk should definitely factor into your decision-making.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency impacts power consumption and operational cost. OLED panels can be more energy-efficient, especially when displaying darker images, as they use less power with black pixels. LCDs consume more energy by necessity due to constant backlighting.
Cost
The cost is a significant factor for many buyers. OLED screens usually come with a higher price tag due to advanced technology and superior performance in several aspects. LCDs are more budget-friendly and offer a performance that can suit many everyday needs.
OLED Vs LCD – Comparison Table
| Feature | OLED | LCD |
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite | Limited by backlight |
| Color Gamut | Wide, vibrant colors | Good, varies by panel type |
| Black Levels | True blacks | Can appear grayish |
| Resolution | Up to 8K | Up to 8K |
| Refresh Rate | Typically higher | Varies by panel type |
| Brightness | Good, but lower in bright light | High, performs well in bright environments |
| Viewing Angles | Wide, consistent | Limited, especially in TN panels |
| Response Time | Faster | Good, varies by panel type |
| Lifespan | Shorter, risk of burn-in | Longer, stable performance |
| Burn-in Risk | Higher | Lower |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower power consumption | Higher power consumption |
| Cost | Higher, premium pricing | Lower, more affordable |
OLED Vs LCD Display: Which Display Technology Is Right for You?
When to Choose OLED:
- If you’re aiming for high-end devices like premium TVs or smartphones.
- When you want vibrant colors and true blacks.
- If watching in a darker room is more your style.
When to Choose LCD:
- If you’re on a budget and need a more economical choice.
- LCDs will serve you better in bright environments due to high brightness levels.
- They have a longer lifespan and are less prone to burn-in issues.