The world of display technology has seen significant advancements, with TFT and OLED screens representing two leading options. Understanding the differences between these technologies can help you make an informed decision when considering your next device.
When comparing TFT and OLED screens, several key differences must be considered. TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) screens are valued for their cost-effectiveness and longer lifespan. However, they rely on a backlight since the liquid crystals do not emit light on their own. In contrast, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) screens deliver richer colors and superior contrast, as they emit their own light, eliminating the need for a backlight. This not only enhances visual quality but can also allow for thinner displays.
In this article, we will compare the two types of screens across various aspects.
Key Takeaways
- TFT offers stability and cost-effectiveness.
- OLED provides superior color and contrast.
- Your choice should depend on usage needs.
TFT Display Technology
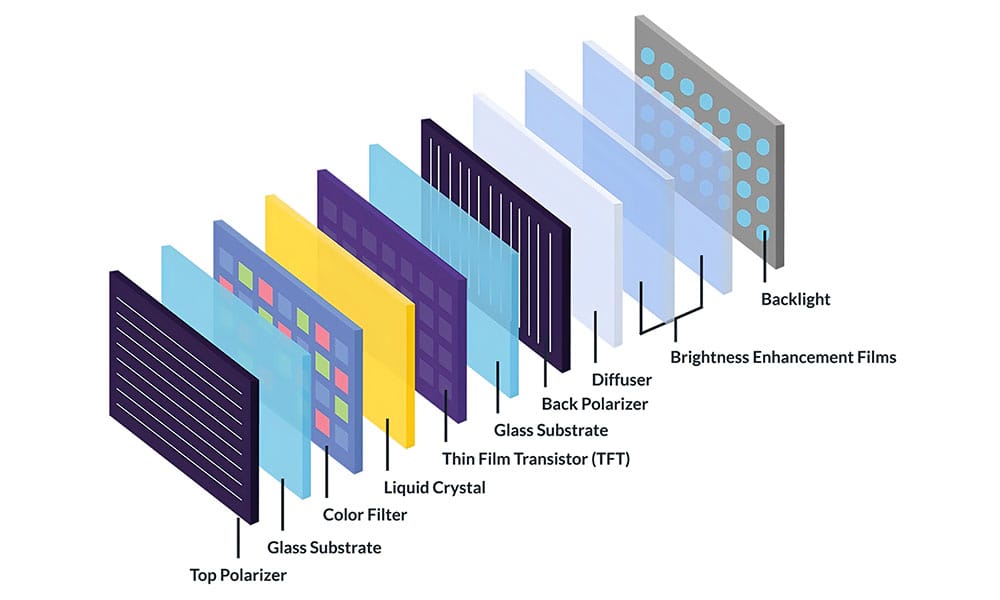
TFT (Thin Film Transistor) is a type of LCD. It operates by using transistors to control individual pixels, allowing precise control over the display output. It works by manipulating liquid crystals, which modulate light from a backlight to create images.
TFT screens come in various types, including IPS (In-Plane Switching), TN (Twisted Nematic), and VA (Vertical Alignment).
Advantages
TFT screens are cost-effective due to cheaper manufacturing processes, making them accessible for a range of devices. With their high brightness, they perform well in bright settings, such as outdoors.
Another advantage is their resilience against burn-in. Unlike OLEDs, static images do not cause lasting imprints on TFT screens, ensuring a longer lifespan without image retention issues.
Disadvantages
One disadvantage of TFT screens is their limited viewing angles, meaning color accuracy and contrast worsen when viewed from the side.
They also have lower contrast ratios, which makes achieving deep blacks difficult compared to OLEDs. In addition, power consumption can be high, as they require constant backlighting to maintain image visibility, unlike self-emitting technologies such as OLEDs.
Applications
TFT screens are widely used in consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, providing dependable display solutions that balance cost and performance.
In industrial displays, they are common in control panels and medical equipment, where reliability and durability are key.
TFT screens are also popular in the automotive industry. They are used in instrument clusters and infotainment systems, offering drivers clear and bright displays essential for vehicle control and entertainment.
OLED Display Technology
OLED stands for Organic Light-Emitting Diode. This technology uses organic compounds that light up when electricity flows through them. Unlike traditional displays, OLED screens do not need a backlight. Each pixel in an OLED screen lights up independently, allowing for deeper blacks and brighter colors. This independent pixel illumination means that dark areas of an image can be truly black, enhancing the overall contrast.
Advantages
OLED displays offer true blacks and impressive contrast ratios. With each pixel emitting its own light, blacks are produced by turning off pixels, creating unparalleled contrast. Colors are vivid, providing a more life-like viewing experience.
Another advantage of OLED screens is wider viewing angles. Colors and brightness remain consistent even when viewed from the side, making OLED ideal for shared viewing experiences.
OLED’s flexible design capabilities allow for innovative displays. Manufacturers can create curved or flexible screens, giving designers new possibilities in device aesthetics and ergonomics.
Disadvantages
Despite their benefits, OLED screens are more expensive to manufacture than traditional displays, making them a premium option.
OLED technology has a risk of burn-in, where static images can cause permanent shadows on the screen. While newer methods reduce this, it’s a consideration if static content is displayed often.
OLED screens may have a shorter lifespan than TFT screens. The organic materials in OLED screens can degrade, leading to reduced brightness or uneven color distribution over time.
Applications
OLED is widely used in consumer electronics. High-end smartphones, televisions, and wearables often use OLED for their superior display qualities.
In the automotive industry, OLEDs are favored for premium displays. They enhance the look of instrument clusters and infotainment systems with their sharpness and flexibility.For digital signage, OLED provides vibrant and eye-catching displays. They’re used in advertising and information fronts where eye appeal is crucial. OLED displays help capture attention, which is vital in these applications.
Comparison of TFT and OLED Screen
In this section, you will explore the contrast ratios, viewing angles, and power consumption of TFT and OLED screens. Discover how these technologies differ in terms of color accuracy, black levels, light emission, brightness, lifespan, and cost.

Contrast Ratio
TFT contrast ratio is primarily limited by the backlight. This means that the range between the darkest and brightest parts of the display is more restricted.
OLED contrast ratio is significantly better because each pixel emits its own light. This enables true blacks and an effectively infinite contrast ratio. You will note the rich and deep colors that OLED can deliver due to this capability.
Viewing Angle
A TFT viewing angle is generally narrower, especially with TN panels. Viewing the screen from an angle often results in color shifts and reduced image quality.
In contrast, an OLED viewing angle is much wider. OLED screens maintain consistent color and brightness even when viewed off-axis, making them more suitable for shared viewing experiences.
Power Consumption
TFT power consumption tends to be higher as it requires constant backlighting, regardless of the content displayed. This means that battery life can be impacted more heavily in mobile devices.
OLED power consumption varies with the content displayed, often being lower when showing dark images. This energy efficiency can enhance battery life, particularly in devices that use dark themes.
Color Accuracy
TFT color accuracy is good but can vary by the type of panel used. IPS panels offer better color reproduction compared to standard TN panels.
OLED color accuracy is exceptional, and it is known for producing vibrant colors. This makes OLED screens particularly attractive for tasks where color precision is crucial, like photo editing.
Black Levels
In a TFT black level, blacks are not truly black due to the backlight, resulting in somewhat washed-out dark tones.
OLED black levels are superior, offering true blacks as the pixels can turn off completely. This leads to more realistic and deeper dark scenes in movies and games.
Light Emission
TFT light emission relies on a backlight to illuminate the screen. This can contribute to a less uniform distribution of light across the display.
OLED light emission is based on self-emitting pixels, which provides a more uniform light distribution and the ability to light only the needed pixels.
Lifespan
TFT screens generally have a longer lifespan and deliver stable performance over time. They are also less prone to issues related to prolonged usage.
An OLED lifespan can be shorter due to risks like burn-in and color degradation. This may affect the long-term usability of an OLED screen if static images are displayed frequently.
Cost
The TFT cost is usually lower. This makes it a more budget-friendly option, suitable for a wide range of devices and applications.
OLED cost is higher due to the complex technology involved. This often places OLED screens in the premium segment, reflecting their advanced features and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the differences and benefits of TFT and OLED screens can help you make informed choices for your devices. Consider factors such as energy use, durability, and visual quality to determine which screen technology meets your needs.
What are the key differences between TFT and OLED screen technologies?
TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) is a type of LCD screen technology, while OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) involves individual pixels emitting their own light. TFT uses backlighting, which can affect contrast and color vividness, whereas OLED offers better contrast with true blacks since the pixels can turn off completely.
How do power consumption rates compare between TFT and OLED displays?
OLED screens generally consume less power than TFT screens when displaying dark images because OLED pixels can turn off individually. TFT screens, which rely on constant backlighting, tend to use more energy overall, especially for darker visuals.
What are the pros and cons of TFT screens compared to OLED screens?
TFT screens are cost-effective and have a longer lifespan. They provide good image quality and perform well in bright environments. OLED screens offer deeper blacks, higher contrast, and more vibrant colors, but they can be more expensive and may suffer from burn-in over time.
Can you compare the visual quality of TFT and OLED screens?
OLED screens typically provide superior visual quality, with richer colors and higher contrast ratios. They deliver more vibrant and true-to-life images compared to TFT screens, which can appear less vivid due to their reliance on backlighting.
In terms of durability, how do TFT screens stack up against OLED screens?
TFT screens usually have greater durability, with a longer shelf life and resistance to image burn-in. OLED screens, while offering excellent visual experiences, are more susceptible to screen burn-in and can degrade faster over time with extended use.
Are there any specific benefits of using OLED screens in laptops over TFT panels?
OLED screens in laptops can provide improved picture quality with better colors and contrast, enhancing visual experiences like streaming and gaming. Their thinner profile can lead to lighter, more portable devices, but they might come at a higher cost than TFT panels.