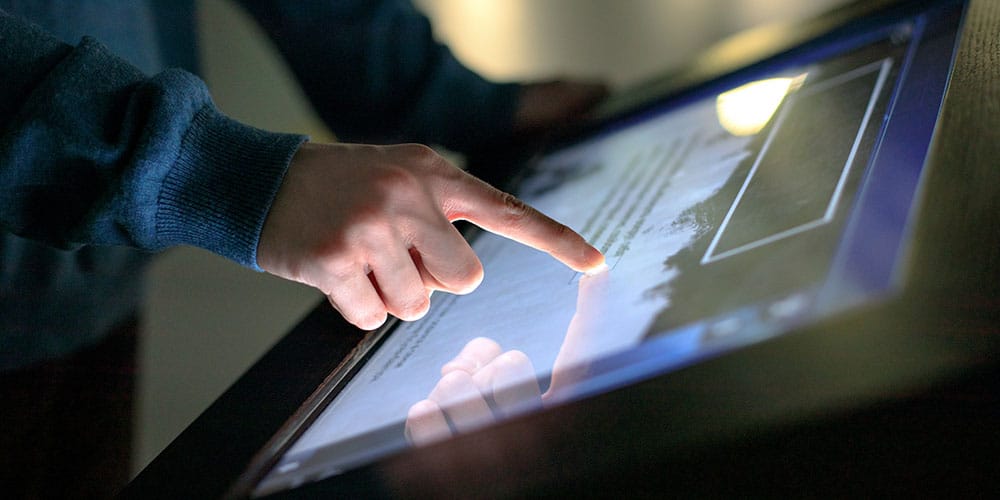
There are seven types of touch screen technology that we encounter in our daily lives, each with unique characteristics suited to different applications. However, capacitive and resistive touchscreens dominate the main market.
Capacitive screens are known for their high responsiveness and ability to support multitouch gestures, such as pinching to zoom. They are widely used in smartphones and tablets due to their accuracy and ease of use. In contrast, resistive touchscreens require more pressure to operate and are often found in environments where durability is essential, such as industrial settings.
In this article, we will explore the two types of touchscreens and highlight the differences between them.
Key Takeaways
- Capacitive screens are responsive and support multitouch.
- Resistive screens are durable and work with more pressure.
Capacitive Touchscreen (PCAP)
A capacitive touchscreen uses the electrical properties of the human body to detect touch. Unlike resistive touchscreens, it does not require pressure. The screen operates by sensing changes in an electrostatic field and is commonly found in smartphones, tablets, ATMs, and kiosks. This type of technology is favored for its responsiveness and capability to register multiple touch gestures.
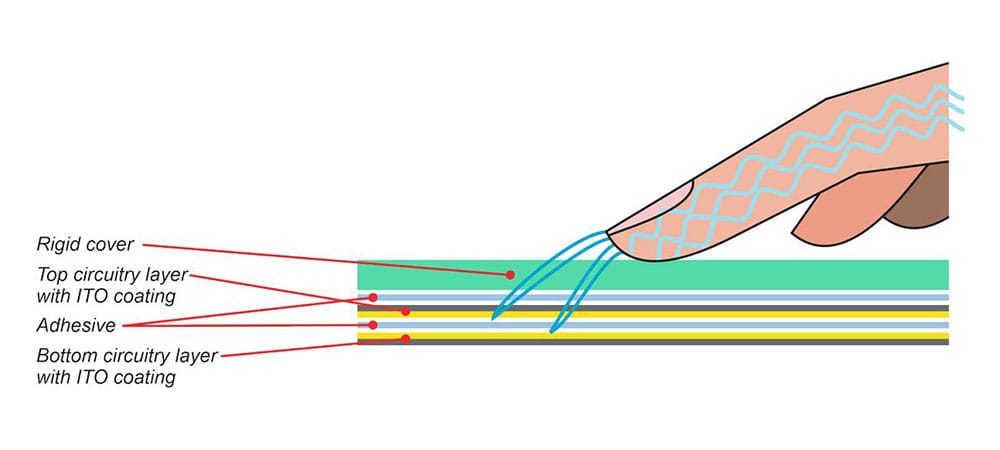
How Do Capacitive Touchscreens Work?
Capacitive touchscreens work by creating an electrostatic field across the screen surface. The screen consists of layers of glass or plastic substrate with a conductive coating such as indium tin oxide (ITO). When you touch the screen, it distorts the electrostatic field, and sensors detect this change. The touchscreen controller then processes this data to interpret the touch location and gestures. Capacitive screens often have a protective cover to enhance durability while maintaining touch sensitivity.
Capacitive Touchscreen Advantages
The high sensitivity of capacitive screens allows them to respond to the slightest touch. They support multi-touch functionality, enabling gestures like swipe, pinch, and zoom. Capacitive touchscreens are durable, resistant to scratches, and contaminants. They provide excellent image clarity and high light transmittance, making them ideal for consumer electronics with high-resolution displays.
Capacitive Touchscreen Disadvantages
Capacitive touchscreens are typically more costly due to their complex technology. They often struggle with input from gloves or styluses unless specially designed. The need for conductive touch can limit their use in some environments, such as scenarios with gloves. Additionally, their sensitivity to moisture can result in false touches if water or other conductive substances are on the screen.
When To Choose A Capacitive Touchscreen
Choosing a capacitive touchscreen is ideal for high-end consumer electronics and devices where touch sensitivity and image clarity are critical. Consider capacitive screens for smartphones, tablets, and medical devices. If your budget allows for advanced features, and the environment is not too moist or dusty, capacitive touchscreens are a strong choice.
Resistive Touchscreen
A resistive touchscreen is a touch-sensitive device that uses pressure for input detection. Unlike capacitive types, which rely on electrical conductivity, these screens respond to any form of pressure, making them versatile.
They are commonly found in industrial controls, medical equipment, and ATMs. These applications often require the screen to function regardless of input method, supporting tools like styluses and gloved fingers.
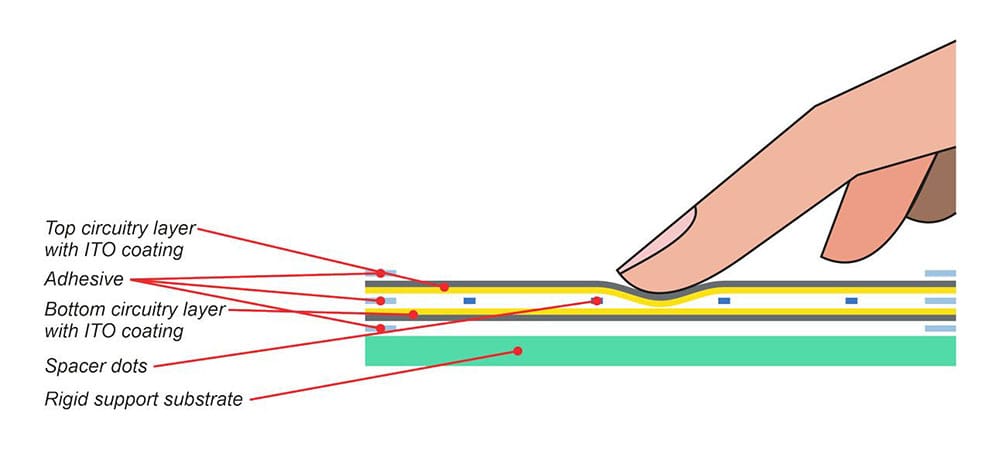
How Do Resistive Touchscreens Work?
Resistive touchscreens operate using two flexible layers separated by a small gap. Each layer is coated with a conductive material. When you apply pressure, the layers make contact at the touched point, causing a change in voltage.
This change is interpreted as a touch. Key components include the top and bottom layers, conductive coatings, and spacer dots that prevent accidental contact. This simple yet effective design makes them reliable in various conditions.
Resistive Touchscreen Advantages
These screens are cost-effective due to their simpler manufacturing process, making them cheaper than capacitive screens. They work with any input device, including a finger, stylus, or glove.
Resistive screens are also resistant to contaminants like dirt and moisture, making them ideal for harsher environments. You can rely on them in dusty or wet conditions, where other touchscreens might fail.
Resistive Touchscreen Disadvantages
Resistive touchscreens require more pressure for activation, leading to lower sensitivity. This means they are less responsive compared to capacitive touch technology.
They also have limited or no multi-touch capabilities, often only supporting a single touch at a time. Additionally, these screens tend to reduce image clarity due to lower light transmission, which can affect visibility.
When To Choose A Resistive Touchscreen
You should consider resistive touchscreens when working in industrial or medical environments where durability and input flexibility are crucial. They perform well outdoors, in rugged settings, and where contamination might be an issue.
Take into account your specific needs, such as budget constraints, the physical environment, and the required features, like precise input using gloves or tools. These factors will guide your decision on choosing this touch technology.
Capacitive vs Resistive Touch

Activation Type
Capacitive: Capacitive touch screens detect touch through the electrical properties of the human finger. They rely on the electrical charge to sense a touch, which makes them highly responsive to even the lightest contact.
Resistive: Resistive touch screens require actual pressure to register input. This is achieved by pressing layers of the screen together, making them less sensitive but suitable for environments where you might use a stylus or gloved hand.
Surface Material
Capacitive: These screens are typically made of glass or hard plastic, which gives them a smooth and sleek appearance. This material is also quite durable, enhancing longevity and maintaining clarity over time.
Resistive: Commonly constructed with flexible plastic or glass, resistive screens can adapt to various input methods. The surface is softer than that of capacitive screens, allowing for better pressure registration but also making them more prone to scratches.
Cost
Capacitive: Generally, capacitive screens are more expensive to produce. The technology and materials are costlier, which reflects in the final price of devices featuring these screens, often making them a choice for high-end products.
Resistive: Due to their simpler manufacturing process, resistive screens come at a lower cost. This makes them popular in budget-friendly applications where high precision and multi-touch are not required.
Touch Sensitivity
Capacitive: Capacitive touch screens are known for their high sensitivity. They respond effortlessly to a light touch, providing a smooth and quick user experience, especially in applications requiring swift navigation.
Resistive: With resistive screens, you need to apply pressure for interaction. This can affect speed but allows greater versatility with different input devices like styluses or gloved hands, preferred in many industrial applications.
Brightness and Contrast
Capacitive: These screens offer excellent brightness and contrast, which enhances visibility even in bright environments. This quality makes capacitive screens ideal for outdoor use or brightly lit indoor spaces.
Resistive: While generally offering lower brightness and contrast compared to capacitive touch screens, resistive screens still provide sufficient visibility for many environments. This makes them a practical choice for uses where lighting is controlled or less critical.
Durability
Capacitive: The glass and robust materials used in capacitive screens make them more resistant to scratches, offering better durability over the long term. This makes them suitable for devices experiencing frequent use.
Resistive: Although they can handle rougher environments, resistive touch screens can wear out faster. The layers may degrade over time, especially with heavy or frequent use, requiring more maintenance or replacements.
Capable of Multi-Touch
Capacitive: This technology supports multi-touch, allowing for gestures like pinching and zooming. It’s a prime feature in tablets and smartphones, enhancing interactive capabilities and user engagement.
Resistive: Generally, resistive screens do not support multi-touch features. Their design focuses more on single-point contact, which limits the complexity of interactions available.
Can Gloves, Pen or Stylus Be Used?
Capacitive: Typically, capacitive screens react less to inputs like gloves or styluses unless specifically designed for these items. This limitation can affect usability in colder climates where gloves are necessary.
Resistive: These screens can accommodate any input, including gloved fingers, pens, and styluses. This flexibility makes them suitable for industrial and medical environments where precision tools are necessary.
Uses
Capacitive: You often find capacitive touch screens in consumer electronics like smartphones and tablets. Their sleek design and responsive touch make them popular in high-end devices.
Resistive: Ideal for industrial, medical, or outdoor applications, resistive screens provide reliable performance where rough handling might occur. Their broad input capability makes them versatile tools across various fields.