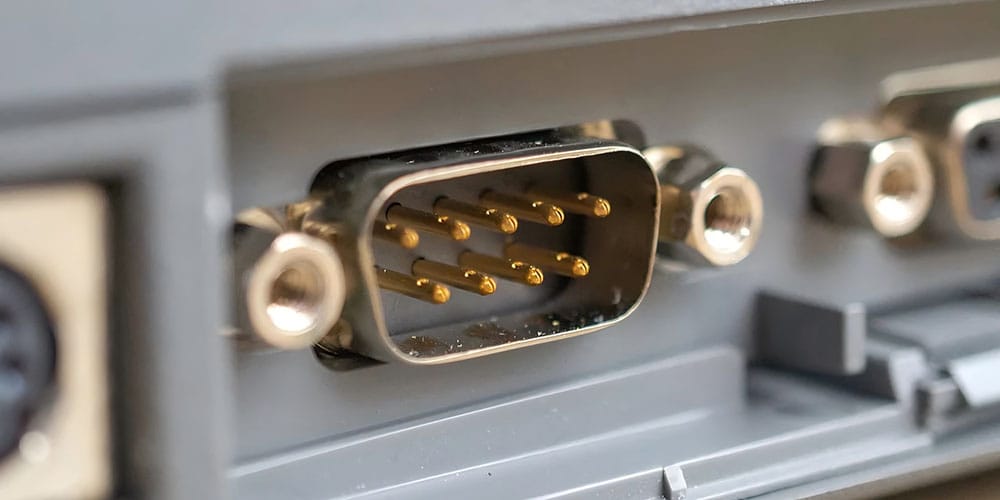
Understanding the ins and outs of computer hardware can sometimes feel like unraveling a mystery. When it comes to connecting devices to your computer, COM ports play a significant role. A COM port is an interface that connects a serial device to a computer, enabling communication between the two. Though technology has evolved, COM ports remain important, especially in technical fields and various industries.
COM ports have been around since personal computers became popular. They’re often associated with RS232 connections, which are crucial for transferring data. Though USB has largely replaced these ports for many consumer applications, COM ports still find their place in areas where stable, direct communication is necessary.
Key Takeaways
- COM ports connect serial devices to computers.
- They are crucial for direct data communication.
- Essential in specialized and technical settings.
What Is A COM Port
A COM port, also known as a serial port, is a key component in computing. Originating with the IBM PC, COM ports were widespread in the 1980s and 1990s. They still play a role today, especially in specialized applications where USB has not completely taken over.
How Do COM Ports Work?
COM ports transmit data one bit at a time via sets of pins. Such as TX (Transmit), RX (Receive), GND (Ground), and control lines.
When data is sent through a COM port, it follows a structured format. There is a start bit, followed by data bits, a parity bit for error checking, and a stop bit to signal the end. This order ensures accurate communication. An example of this is connecting a modem to a computer, allowing them to exchange data smoothly.
What Is A Serial Interface?
A serial interface enables communication by sending data as a stream of individual bits. There are two main types: asynchronous and synchronous. Asynchronous interfaces, like RS-232, send data without needing continuous signals, while synchronous interfaces such as SPI and I2C match the data rate with clock signals.
In contrast to parallel interfaces, which transmit multiple bits simultaneously, serial interfaces manage data one bit at a time. Although serial interfaces can be slower, they are simpler and use fewer wires, making them ideal for longer distances.
Types Of Serial Ports
There are several types of serial ports, each suited for different tasks. The RS-232 is a widely recognized standard in serial communications. You’ll often find it used in computer systems and networking.
For industrial environments, the RS-485 is popular due to its ability to handle multiple devices over longer distances. The RS-422 is similar to the RS-485 but with distinct electrical traits.
Common connectors for these ports include the DE-9 and DB-25 connectors. Despite the dominance of USB, devices still use USB-to-serial adapters to connect to serial ports, maintaining compatibility with older systems.
Serial Communication Protocols
Serial communication uses various protocols to ensure effective data transfer. RS-232, RS-485, and RS-422 are some prominent examples. Other protocols like SPI and I2C support synchronous communication with more complex devices.
These protocols can operate in different modes: Simplex (one-way communication), Half Duplex (two-way communication but one direction at a time), and Full Duplex (simultaneous two-way communication). Error control is critical, managed through parity bits and start/stop bits. For instance, RS-232 is often used in point-of-sale systems due to its reliability.
What Is A Serial Device?
A serial device communicates using a serial interface, transmitting data bit by bit. Examples include modems, printers, and various scientific instruments. These devices often feature characteristics that suit specific applications, like data being processed slowly but accurately.
You’ll find serial devices used in industrial automation, allowing machines to communicate efficiently. They also play a significant role in fields requiring precise data transfer, such as scientific research, where devices must relay exact measurements over considerable distances.
What Are Serial Ports Used For?
Serial ports serve various purposes in connecting devices to your computer. They are often used to connect modems, sending and receiving data over phone lines. Many older mice also connect through serial ports. While less common today, some printers still use serial ports for basic tasks.
In industrial settings, serial ports play a vital role. They connect to automation systems and have applications in scientific instruments. Serial ports help ensure reliable communication between machines in these environments.
Despite the rise of USB, serial ports maintain relevance in modern applications. They are used in specific tasks where a simple, direct connection is needed. In some networking scenarios, serial ports assist in console management for routers and switches.
Parallel ports are related but different, typically used for older printers and sometimes scanners. They provide a parallel communication path, unlike the sequential data transfer in serial ports. Though less common now due to USB, both serial and parallel ports remain useful in niche applications.
The Role Of COM Ports In Serial Communication
COM ports serve as an I/O interface that connects serial devices to computers, allowing data to be sent and received efficiently. This method of communication is both reliable and straightforward, making it a preferred choice in many applications.
COM ports prove invaluable in diagnostics and configuration. They are often used in server consoles and various networking hardware. For instance, they can connect directly to networking devices such as routers and switches, enabling easy configuration.
One common application is configuring routers and switches. When direct network access isn’t possible, a COM port provides a way to make necessary changes to the device settings. Use a terminal emulator to access the device and adjust IP addresses or other configurations as needed.
These ports send data one bit at a time, ensuring precise communication. Each bit’s journey starts with a start bit and ends with a stop bit. This process allows COM ports to establish point-to-point solid connections between devices, which is essential in many industrial and networking environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I identify which COM port I am using on my system?
To find out which COM port you are using, open the Device Manager. Look for “Ports (COM & LPT)” and expand it. You will see a list of COM ports such as COM1 or COM2. The device connected to each port will also be displayed here.
What purposes does a COM port serve in modern computing?
COM ports facilitate communication between your computer and peripheral devices. They are commonly used for industrial equipment and legacy hardware connections. Despite the rise of USB, these ports remain vital for certain applications that require stable, point-to-point communication.
What are the distinctions between serial ports and COM ports?
A COM port is essentially a type of serial port. While all COM ports are serial ports, not all serial ports are labeled as COM. The distinction often relates to the interface and use on PCs. COM ports are specifically used by Windows for RS232 communication.
Can USB ports be utilized as COM ports, and if so, how?
Yes, USB ports can be used as COM ports with the help of USB-to-serial converters. These converters allow USB ports to emulate COM ports, enabling connection to serial devices. This is useful when your system lacks dedicated COM ports.
How is a COM port connector typically integrated into a motherboard?
On a motherboard, COM ports are usually connected via an ISA card or directly integrated into it. They may use an IRQ and specific resources like addresses to function. These settings can sometimes be adjusted through the BIOS or by moving the port to a different ISA slot.