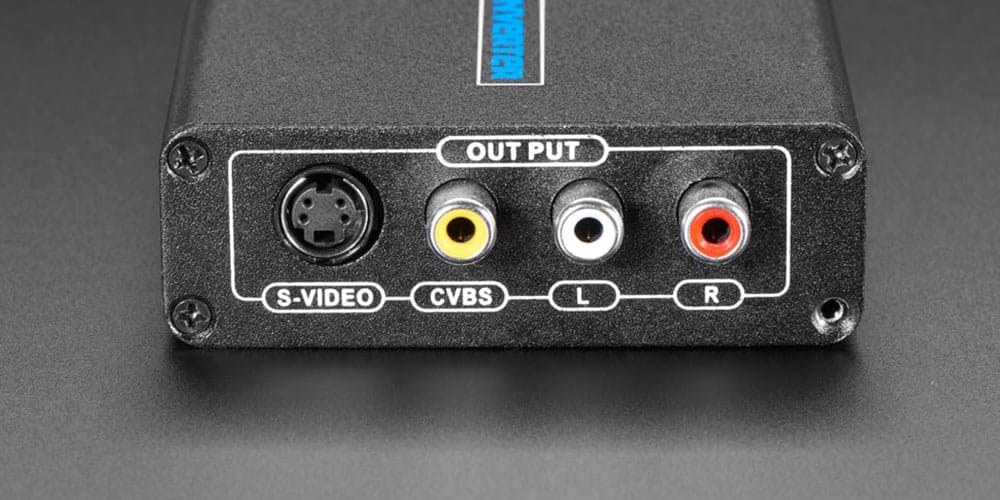
A CVBS port might sound technical, but if you’ve dealt with any older video equipment, you’ve likely encountered it. It’s often tied to RCA connectors, serving as the backbone of analog video. But what exactly is a CVBS port?
A CVBS port, or Composite Video Blanking and Sync port, is an analog video connection used for transmitting standard-definition video signals. Widely found on older TVs and video devices, it offers a simple way to display video content without audio on compatible screens.
Let’s dive deeper into CVBS and its common uses, connections, and why it’s still relevant today.
What Is the Purpose of CVBS?
The CVBS port was primarily designed to transmit standard-definition video, providing a universal way to share video signals between devices. While limited in resolution, it was instrumental in the early days of video technology.
The purpose of the CVBS port is to transmit analog video signals without audio, ideal for displaying standard-definition content on compatible screens.
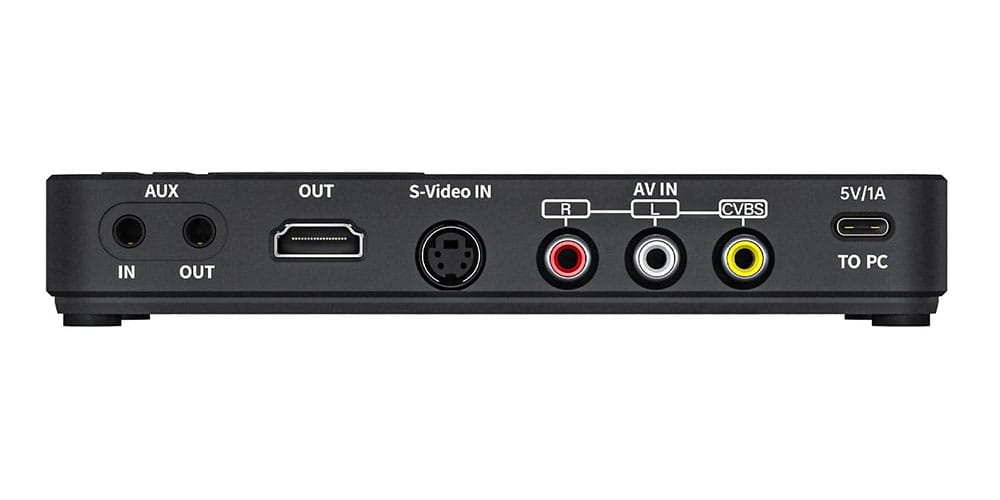

Despite its age, CVBS ports are still common in legacy video setups, from old gaming consoles to security cameras. By consolidating the video signal into one line, it avoids the complexity of component or HDMI connections, making it straightforward for users.
Is CVBS the Same as RCA?
You may have seen RCA connectors linked to CVBS, and it’s easy to think they’re the same. However, RCA is the type of connector, while CVBS describes the video signal that travels through it.
No, CVBS and RCA are not the same. RCA is the physical connector, while CVBS describes the video signal type transmitted through RCA cables.
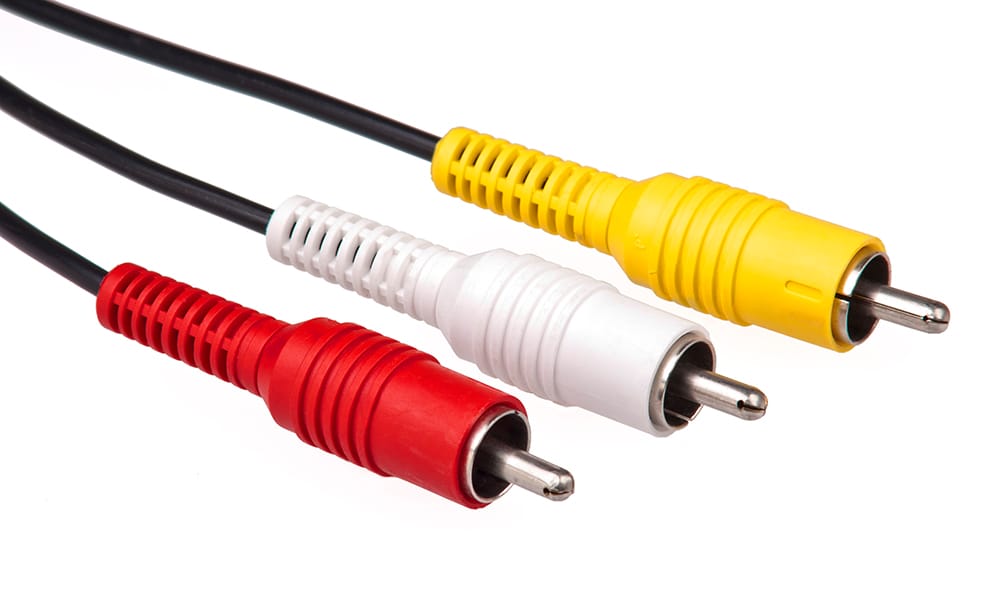

RCA connectors typically carry the CVBS video signal on a yellow plug, along with separate red and white plugs for audio. But in reality, RCA connectors can transmit different types of signals, from audio to video, depending on the device. Knowing this distinction helps when setting up old-school equipment, where the yellow RCA connector usually signifies the CVBS video line.
What Does CVBS Mean on a TV?
Seeing “CVBS” on your TV inputs may seem cryptic, but it’s simply the label for composite video. This port accepts analog video signals, usually through an RCA connector, as mentioned.
On a TV, “CVBS” means the input port is ready to receive composite video signals, typically from older video devices.
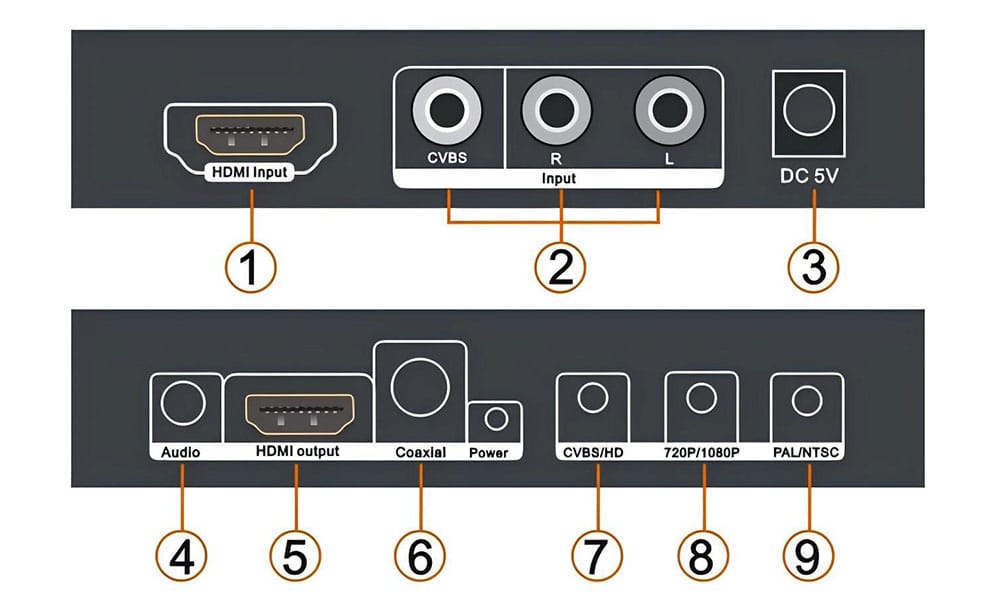
Back in the day, CVBS was the universal format for video inputs on TVs. You’d plug the yellow RCA cable into the CVBS port, ensuring the screen could display content from devices like VCRs, camcorders, or gaming consoles. Though it’s not HD, it offered a reliable viewing option before HDMI became the standard.
How to Connect CVBS to a TV?
Connecting CVBS to a TV is straightforward. Typically, it requires an RCA cable, where the yellow plug carries the video signal, and red and white cables transmit audio.
To connect CVBS to a TV, use an RCA cable. Plug the yellow RCA connector into the TV’s CVBS port, with red and white cables for audio if needed.
Start by identifying the CVBS (or “Video In”) input on your TV. Plug in the yellow RCA connector, ensuring it goes into the yellow video input, and add the audio plugs if applicable. Once connected, switch your TV to the appropriate input source, usually labeled “AV” or “Video,” and you should see the video signal. If the picture quality seems off, it might be due to the low resolution CVBS naturally supports.
What Does CVBS Output Mean?
If you see “CVBS output” on a device, it means the device can transmit video through a composite signal, using a single RCA output for standard-definition video.
A “CVBS output” means the device sends an analog video signal, viewable on screens that accept composite video inputs.
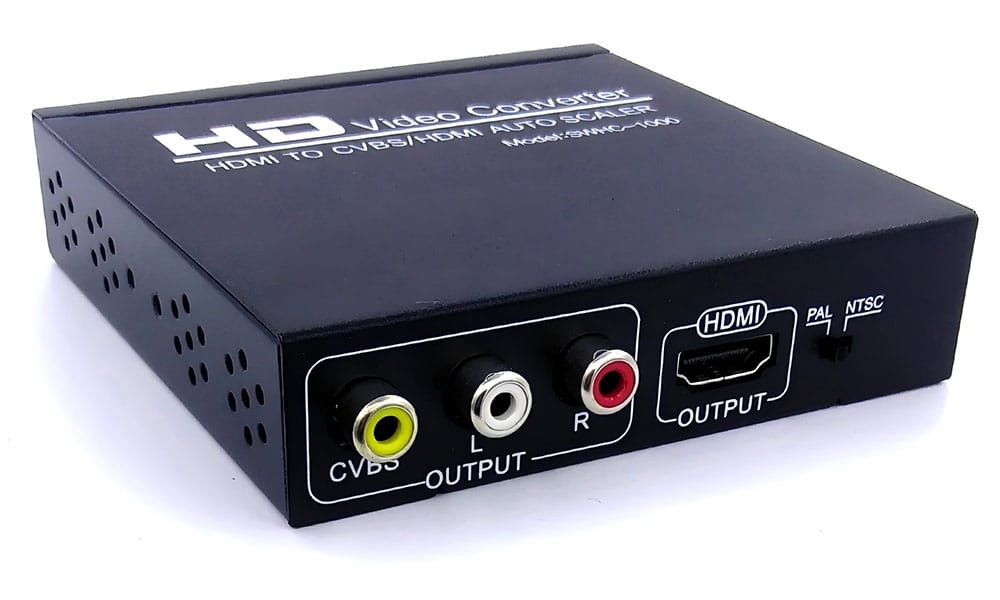

Devices with CVBS outputs are typically older models, like DVD players, VCRs, and some camcorders. By using the CVBS output, these devices can easily connect to compatible screens via a simple RCA cable, making it a reliable option for standard-definition video display.
What Is the Difference Between CVBS and AHD?
AHD, or Analog High Definition, is a newer analog format that offers higher resolution than CVBS. While CVBS is limited to standard-definition, AHD can reach HD quality.
CVBS and AHD differ mainly in resolution: CVBS is standard-definition, while AHD provides high-definition quality, making it preferable for modern analog video setups.

CVBS has been around for decades, while AHD emerged as a higher-quality alternative. For users needing crisp images on analog setups, AHD can be a great upgrade. However, keep in mind that AHD requires compatible devices for full HD playback, while CVBS can work with nearly any legacy screen.
What Is the Resolution of the CVBS Signal?
The CVBS signal is typically limited to 480i or 576i, offering standard-definition video. This may look grainy on modern screens but served well for analog TVs.
CVBS resolution is generally capped at 480i or 576i, supporting standard-definition video with an interlaced signal.
Despite its limited resolution, CVBS was a go-to for analog video setups for years. With a lower refresh rate, it’s not ideal for HD content but remains compatible with most legacy systems. When connecting CVBS to larger screens, remember that the signal may look blurry or pixelated, which is normal for analog SD video.